The diurnal and annual cycle in solar radiation is reflected into air temperature by the absorption of solar radiation.
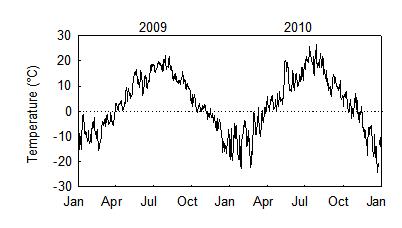
The annual cycle in the radiation generates the annual cycle in temperature. The temperature reaches annual maximum and minimum about one month later than radiation. In the boreal region, soil temperature has a strong seasonal pattern that follows the air temperature.
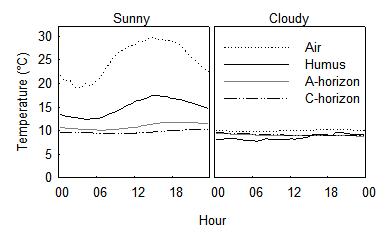
The diurnal cycle in solar radiation is reflected into air temperature by the absorption of solar radiation. The cooling in the evening is a result of thermal radiation to space that predominates during cloudless moments without solar radiation. Therefore, rapid temperature increase and decrease is characteristic for sunny days. Clouds reduce radiation and consequently, the amplitude of temperature change is small.
Ecological studies use a wide collection of temperature measurement technology. However, measuring temperature is difficult, especially with an uncertainty less than 0.1 °C. Radiation introduces larger systematic error than the sensor uncertainty in air measurement and therefore, the used sensor must be properly shielded from radiation. The temperature also changes in time and space (i.e. temporally and spatially, which can cause error). Go to Observations and view the air temperature measurements made at Hyytiälä Forestry Field Station.